Die offizielle Wegleitung zum Studiengang findet ihr hier.
You can find the official guidelines (in german) for the degree programme here.
I. Das Studium / The study programme
Das Masterstudium Geowissenschaften an der Universität Basel vermittelt eine fundierte und praktische Ausbildung.
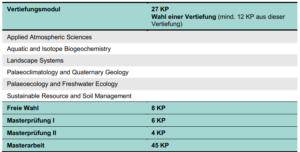
Das Studium gliedert sich in die Module: Applied Atmospheric Sciences; Aquatic and Isotope Biogeochemistry; Landscape Systems; Palaeoclimatology and Quaternary Geology; Palaeoecology and Freshwater Ecology; Sustainable Resource and Soil Management (insgesamt 27 KP, davon mind. 12 KP aus einem gewählten Vertiefungsmodul); Masterarbeit (45 KP); Masterprüfungen (10 KP); Wahlbereich (8 KP).
Mit einem Abschluss BSc Geowissenschaften der Universität Basel erfolgt die Zulassung ohne Auflagen. Die Zulassung für alle übrigen Studienanwärterinnen bzw. -anwärter erfolgt auf Antrag der Prüfungskommission durch das Rektorat.
Informationen zur Zulassung:
https://www.unibas.ch/Zulassung
Die Dauer des Masterstudiums beträgt in der Regel 3 Semester und führt zu einem international anerkannten Abschluss (MSC Geowissenschaften/MSc Geosciences). Hierzu werden Lernmodule in einem Umfang von mindestens 90 Kreditpunkten (KP) absolviert.
Der Beginn des Bachelorstudiums ist im Herbst- und im Frühjahrssemester möglich.
English:
The Master’s programme in Geosciences at the University of Basel provides a sound and practical education.
The programme is divided into the following modules: Applied Atmospheric Sciences; Aquatic and Isotope Biogeochemistry; Landscape Systems; Palaeoclimatology and Quaternary Geology; Palaeoecology and Freshwater Ecology; Sustainable Resource and Soil Management (27 CP in total, of which at least 12 CP from a chosen specialisation module); Master’s thesis (45 CP); Master’s examinations (10 CP); elective area (8 CP).
With a BSc Geosciences degree from the University of Basel, admission is unconditional. Admission for all other prospective students is granted by the Rectorate at the request of the Examination Board.
Information on admission:
https://www.unibas.ch/Zulassung
The Master’s degree programme generally lasts 3 semesters and leads to an internationally recognised degree (MSC Geosciences/MSc Geosciences). This involves completing learning modules totalling at least 90 credit points (CP).
The Bachelor’s programme can be started in the autumn and spring semesters.
II. Aufbau des Studiums / Structure of the study programme
Masterprüfung
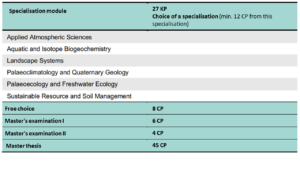
Die Prüfung I dauert 45 Minuten und die Prüfung II 30 Minuten. Die Prüfung I muss durch eine Prüferin bzw. Prüfer aus dem gewählten Vertiefungsmodul («Applied Atmospheric Sciences», «Aquatic and Isotope Biogeochemistry», «Landscape Systems», «Paleoclimatology and Quaternary Geology», «Paleoecology and Freshwater Ecology», «Sustainable Resource and Soil Management»), die Prüfung II durch eine zweite Prüferin bzw. einen zweiten Prüfer frei wählbar innerhalb der Geowissenschaften abgenommen werden. Die prüfenden Personen (habilitiert oder gleichwertig qualifiziert) sind frei wählbar unter den von der Unterrichtskommission zugelassenen Prüferinnen bzw. Prüfern.
English:
Master’s examination
Exam I lasts 45 minutes and Exam II 30 minutes. Examination I must be taken by an examiner from the chosen specialisation module („Applied Atmospheric Sciences“, „Aquatic and Isotope Biogeochemistry“, „Landscape Systems“, „Paleoclimatology and Quaternary Geology“, „Paleoecology and Freshwater Ecology“, „Sustainable Resource and Soil Management“), and Examination II by a second examiner of your choice within the geosciences. The examiners (habilitated or equally qualified) are freely selectable from the examiners approved by the Teaching Committee.
III. Vertiefungen / Specialisations
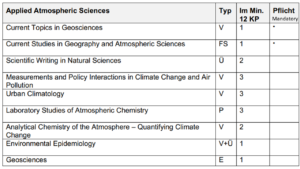
1. Applied Atmospheric Sciences
To the Website of Applied Atmospheric Sciences
Studierende erwerben die Fähigkeit,
- Wechselwirkungen zwischen Erdoberfläche und Atmosphäre sowie die dynamischen Prozesse innerhalb der Atmosphäre zu verstehen und zu erklären.
- Prozesse des Strahlungs- und Energieumsatzes an der Erdoberfläche zu kennen.
- physikalische und chemische Grundlagen der atmosphärischen Prozesse zu verstehen.
- den Einfluss von Luftschadstoffen auf die menschliche Gesundheit und die vor allem vom Menschen verursachten Änderungen des globalen Klimas zu verstehen.
English:
Students acquire the ability to
- Understand and explain interactions between the Earth’s surface and atmosphere as well as the dynamic processes within the atmosphere.
- know the processes of radiation and energy conversion at the Earth’s surface.
- understand the physical and chemical principles of atmospheric processes.
- understand the influence of air pollutants on human health and the changes in the global climate caused primarily by humans.
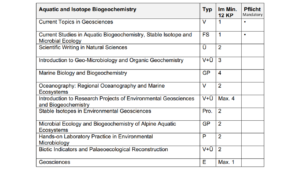
2. Aquatic and Isotope Biogeochemistry
To the Website of Isotope Biogeochemistry
Studierende erwerben die Fähigkeit,
- aquatische Stoff- und Energiekreisläufe zwischen den Ökosystemen verschiedener Geosphären unter Berücksichtigung anthropogener Einflüsse zu untersuchen.
- biogeochemische Stoffkreisläufe in limnischen und marinen Systemen zu kennen und zu erklären.
- Reaktionen von aquatischen Ökosystemen auf Umweltveränderungen und die Folgen für das globale Klima zu verstehen.
- mikrobielle Stoffwechselreaktionen und deren geochemische und molekulare Fingerabdrücke in natürlichen Gewässern und Sedimenten zu kennen.
English:
Students acquire the ability to
- analyse aquatic material and energy cycles between the ecosystems of different geospheres, taking anthropogenic influences into account.
- recognise and explain biogeochemical material cycles in limnic and marine systems.
- understand the reactions of aquatic ecosystems to environmental changes and the consequences for the global climate.
- recognise microbial metabolic reactions and their geochemical and molecular fingerprints in natural waters and sediments.
3. Landscape Systems
To the Website of Landscape Systems
Studierende erwerben die Fähigkeit,
- Die Landschaftssysteme der Erde, deren natürliche Entwicklung, ihre bewusste Gestaltung und unbewusste Veränderung durch die Menschen auf verschiedenen räumlichen Ebenen zu verstehen und zu erklären.
- Die Erdoberfläche als Schnittstelle zwischen Atmosphäre, Boden, Gestein, Gewässern, Vegetation und Tierwelt sowie als Grundlage für das menschliche Leben natur- und sozialwissenschaftlich zu beschreiben.
- Die Folgen des globalen Umweltwandels für Landschaftssysteme sowie damit verbundene Naturgefahren und Risiken für Umweltservices zu kennen und zu verstehen.
English:
Students acquire the ability to
- Understand and explain the Earth’s landscape systems, their natural development, their conscious design and unconscious change by humans at different spatial levels.
- Describe the Earth’s surface as an interface between atmosphere, soil, rock, water, vegetation and fauna and as the basis for human life from a natural and social science perspective.
- Recognise and understand the consequences of global environmental change for landscape systems and the associated natural hazards and risks for environmental services.
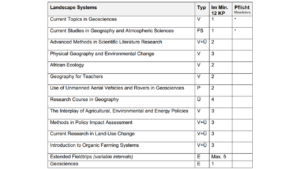
4. Palaeoclimatology and Quaternary Geology
To the Website of Palaeoclimatology and Quaternary Geology
Studierende erwerben die Fähigkeit,
- die Entwicklungsgeschichte und die kontinuierlichen Veränderungsprozesse der Erde in der jüngeren Erdgeschichte zu verstehen und zu erklären.
- oberflächennahe Prozesse, des Gesteins- und Wasserkreislaufs zu kennen und beschreiben.
- Beschaffenheit und Verhalten von Lithosphäre und Hydrosphäre sowie deren Interaktion zu untersuchen.
- geologische Archive und aktuelle Umweltprozesse für die Beurteilung langfristiger Entwicklungen vergleichend zu analysieren.
- die Steuerfaktoren und den Verlauf Quartärer Klimaschwankungen zu erklären und diese mit Hilfe von geochemischen Untersuchungen an verschiedenen geologischen und biologischen Klimaarchiven zu bestimmen.
- Den Einfluss quartärer Klimaschwankungen auf die Evolution, Ausbreitung und Geschichte des Menschen zu beurteilen
English:
Students acquire the ability to
- understand and explain the history of the Earth’s development and the continuous processes of change in recent geological history.
- recognise and describe near-surface processes of the rock and water cycle.
- investigate the composition and behaviour of the lithosphere and hydrosphere and their interaction.
- comparatively analyse geological archives and current environmental processes for the assessment of long-term developments.
- explain the controlling factors and the course of Quaternary climate fluctuations and determine these with the help of geochemical investigations of various geological and biological climate archives.
- assess the influence of Quaternary climate fluctuations on human evolution, dispersal and history
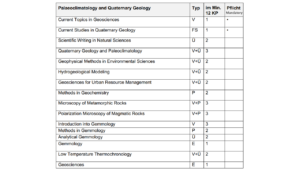
5. Palaeoecology and Freshwater Ecology
To the Website of Freshwater Ecology
Studierende erwerben die Fähigkeit,
- die Ökologie und Biogeographie von Indikatororganismen, die Entwicklung von Ökosystemen oder sich ändernde Artenareale in Vergangenheit und Gegenwart zu kennen und langfristig wie kurzfristiger wirkende ökologische Mechanismen und Prozesse zu verstehen.
- die Reaktion von Ökosystemen, Arten, Populationen und die Biodiversität auf natürliche und anthropogene Umweltveränderungen zu analysieren.
- den Einfluss von frühen und postindustriellen menschlichen Aktivitäten auf Seen und Landschaften zu erklären.
- Ökosystem-Funktionen von Quellen und Fliessgewässern, evolutive Anpassungen von Quellorganismen sowie ihre Verbreitung zu verstehen.
English:
Students acquire the ability to
- know the ecology and biogeography of indicator organisms, the development of ecosystems or changing species ranges in the past and present and understand long-term and short-term ecological mechanisms and processes.
- analyse the reaction of ecosystems, species, populations and biodiversity to natural and anthropogenic environmental changes.
- explain the impact of early and post-industrial human activities on lakes and landscapes.
- understand ecosystem functions of springs and watercourses, evolutionary adaptations of spring organisms and their distribution.
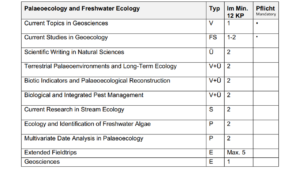
6. Sustainable Resource and Soil Management
To the Website of Resource and Soil Management
Studierende erwerben die Fähigkeit,
- biogeochemische Kreisläufe in terrestrischen Ökosystemen vertieft zu verstehen.
- Stoffkreisläufe in Böden und den Transfer von Stoffen und Energie zwischen Böden, Atmo-, Lithound Hydrosphäre zu kennen und zu erklären.
- aktuelle Umweltprobleme unter dem Aspekt von Klima- und Landnutzungswandel zu untersuchen.
- das Gleichgewicht von Ökosystemen im Spannungsfeld zwischen der Nutzung durch den Menschen und ihrem Schutz zu verstehen.
English:
Students acquire the ability to
- understand biogeochemical cycles in terrestrial ecosystems in depth.
- know and explain material cycles in soils and the transfer of substances and energy between soils, atmosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere.
- analyse current environmental problems from the perspective of climate and land use change.
- understand the balance of ecosystems in the field of tension between their utilisation by humans and their protection.
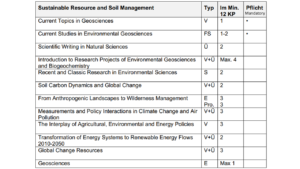
IV. Berufsmöglichkeiten / Career opportunities
Umweltwissenschaftliche Unternehmen, Raumplanung, Ressourcen- und Materialforschung, kantonale Ämter, Bundesämter, Forschungseinrichtungen, staatliche und nichtstaatliche Organisationen, Industrie, Hochschulen, Schulen
English:
Environmental science companies, spatial planning, resource and materials research, cantonal offices, federal offices, research institutions, governmental and non-governmental organisations, industry, universities, schools
______________________________________________
26.02.2024
